So exciting to see your work in actual print! Special shout out to Davis Laundon for pulling chapter 10 together.
BIU Southampton
University of Southampton
Orestis Katsamenis
Rohan Lewis
Tricia Goggin
#vEM


Pleased to share our latest paper 'Convergently evolved placental villi show multiscale structural adaptations to differential placental invasiveness' in Royal Society Publishing #BiologyLetters out now! #placenta #evolution Southampton Medicine Biological Sciences University of Southampton News
royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rs…

Excited to start on new project with Michael Cunliffe 🏳️🌈 MBA - Marine Biological Association MBA Cell and Molecular studying Chytrids Davis Laundon



Check out this amazing set of posts from Davis Laundon about some correlative imaging we did in the BIU Southampton of Southampton Medicine / μ-VIS X-ray Imaging Centre
BioImagingUK
FocalPlane
University Hospital Southampton 💙
VolumeEM
UoS Public Engagement

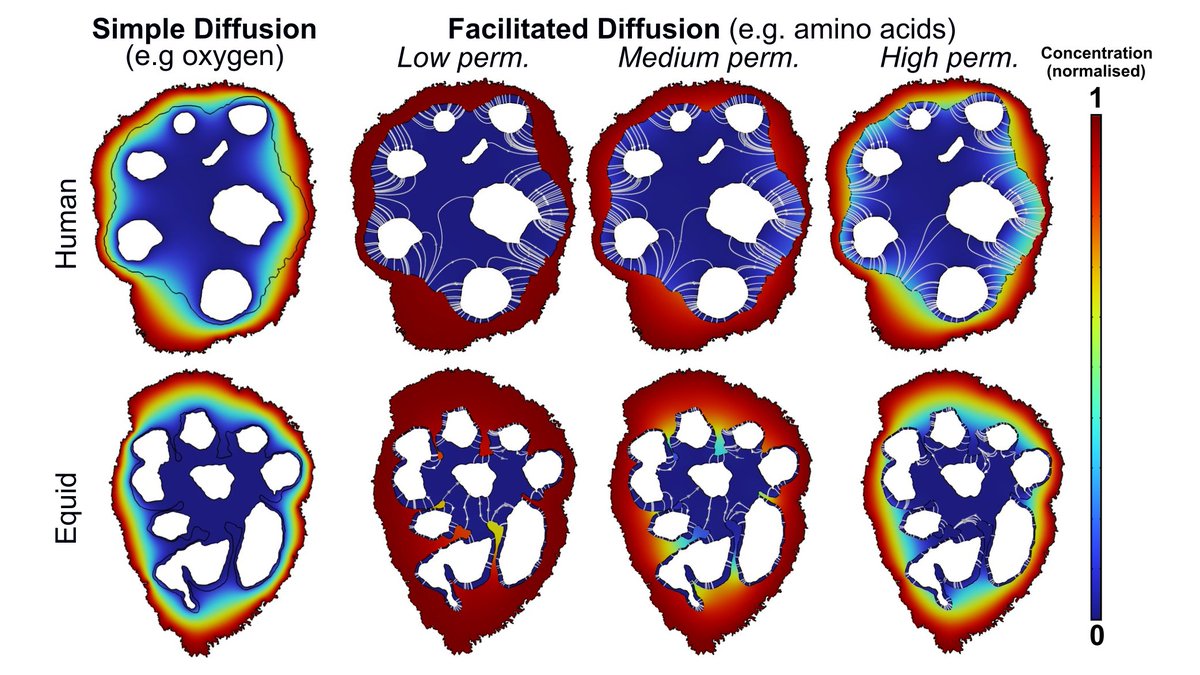
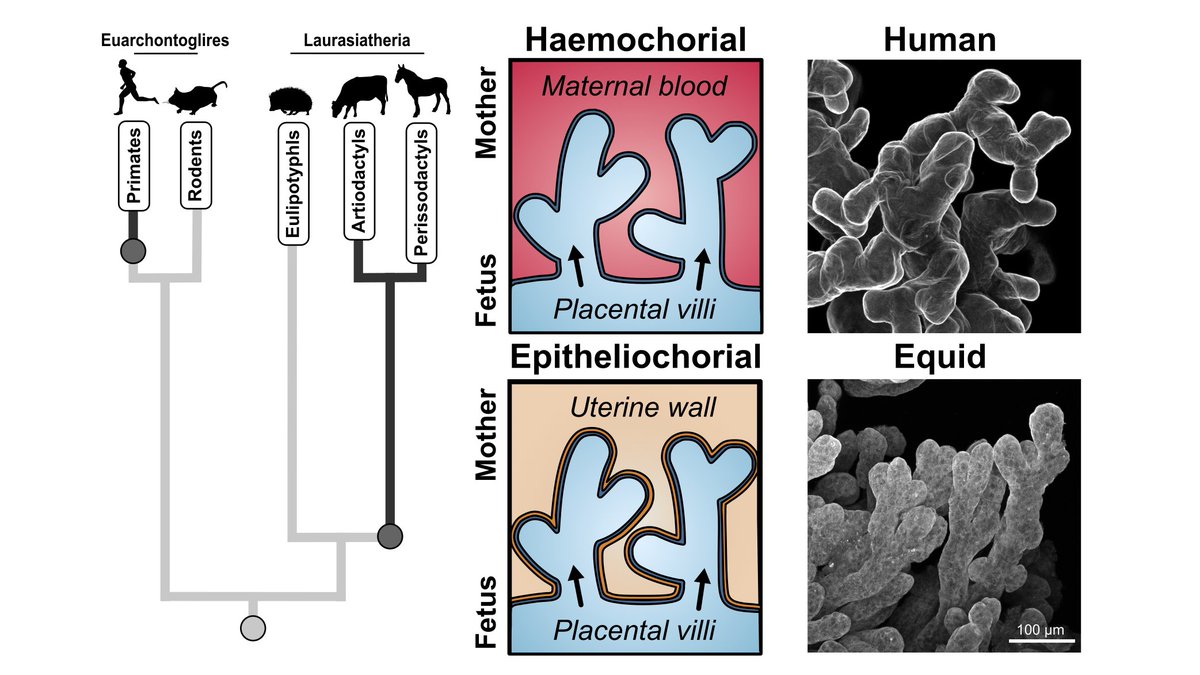
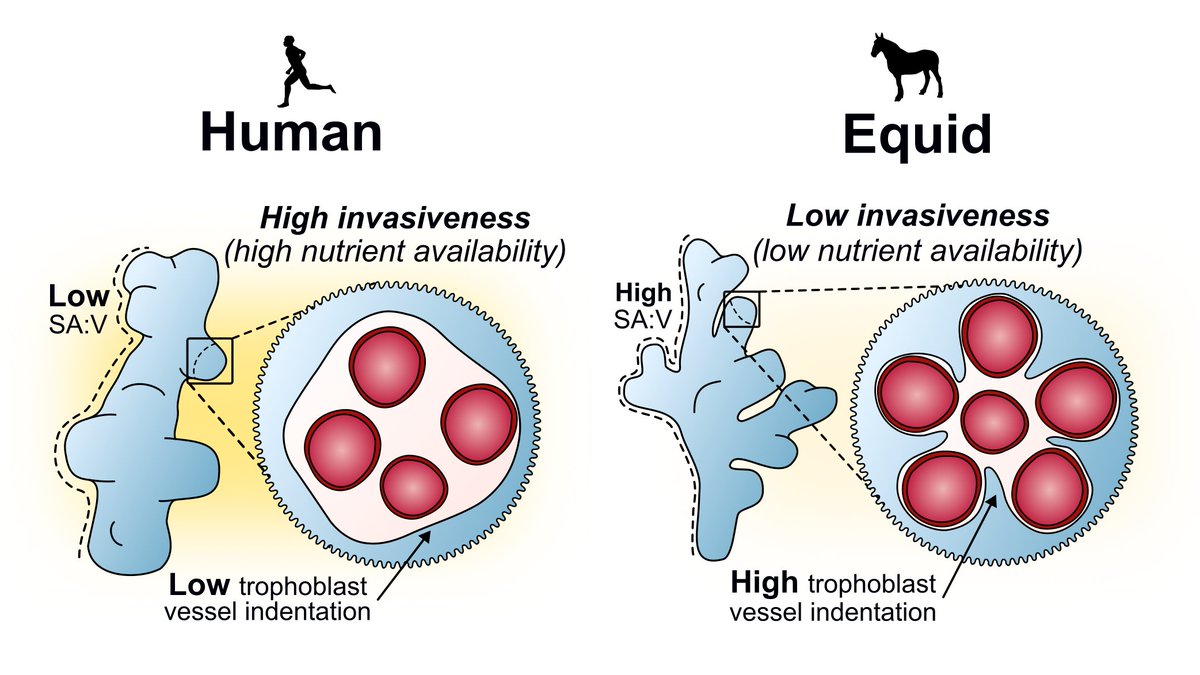
Taken together, we propose the features we have observed in equid villi are adaptations that have evolved in response to low nutrient availability in less 'invasive' equid placentas, suggesting support for maternal-fetal conflict in placental evolution. Rohan Lewis Neil J Gostling

Great to have you Davis Laundon ! Looking forward to seeing the results of your segmentation.

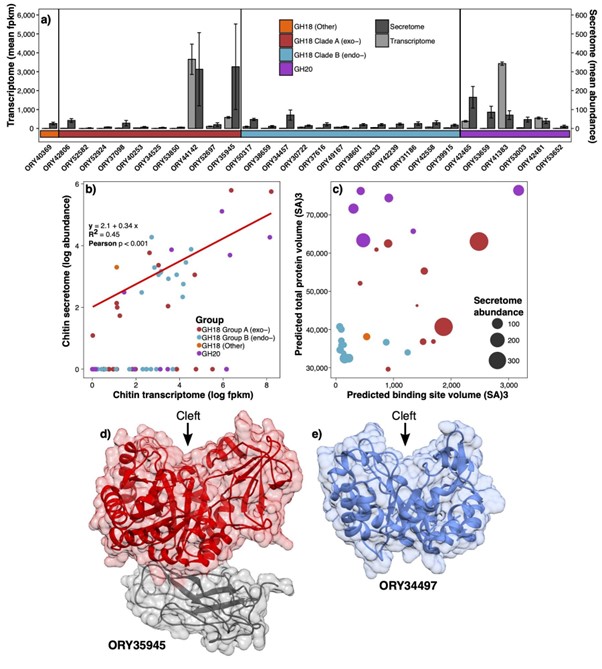
Very pleased to be involved with this great new bioRxiv 'Evolutionary and biological mechanisms underpinning chitin degradation in aquatic fungi' lead by Dr Nathan Chrismas and Michael Cunliffe 🏳️🌈, out now on #DarwinDay ! Dr. Kimberley Bird Dr. Poppy Hesketh-Best Chloe Lieng
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…

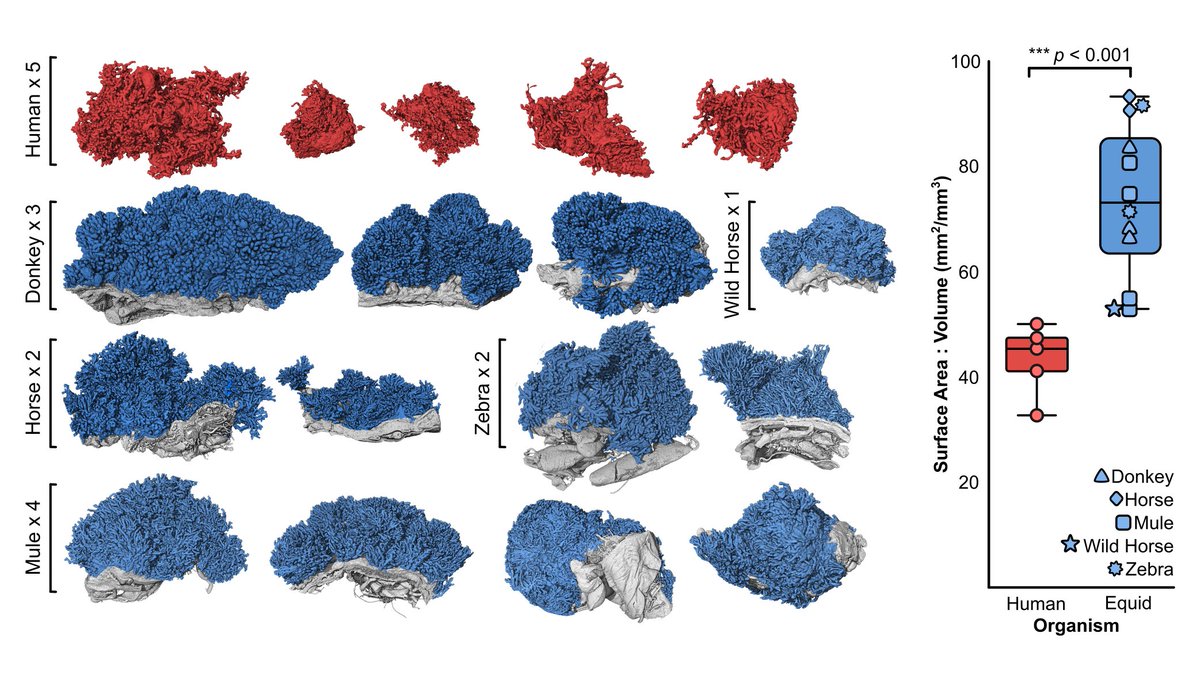
Using #microCT , we imaged in #3D human and equid (horse, donkey, mule, wild horse, & zebra) placental villi and found that equids have a significantly larger surface area for any given volume (SA:V) for nutrient uptake than humans. μ-VIS X-ray Imaging Centre Orestis Katsamenis

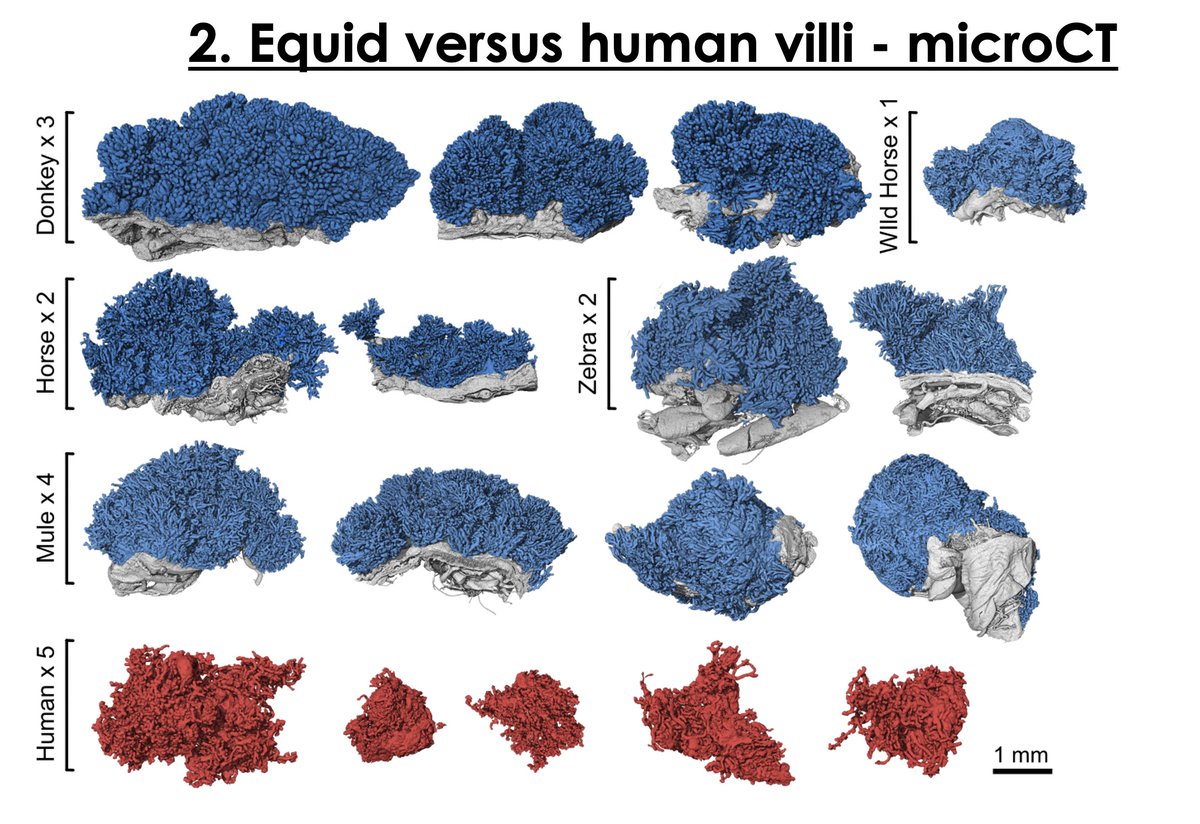
I was excited to present work at IFPA from Davis Laundon in my lab showing the first quantitative comparison of human and equid placental villi and asking really fundamental questions about placental efficiency. If you weren't at IFPA, the paper is in preparation!

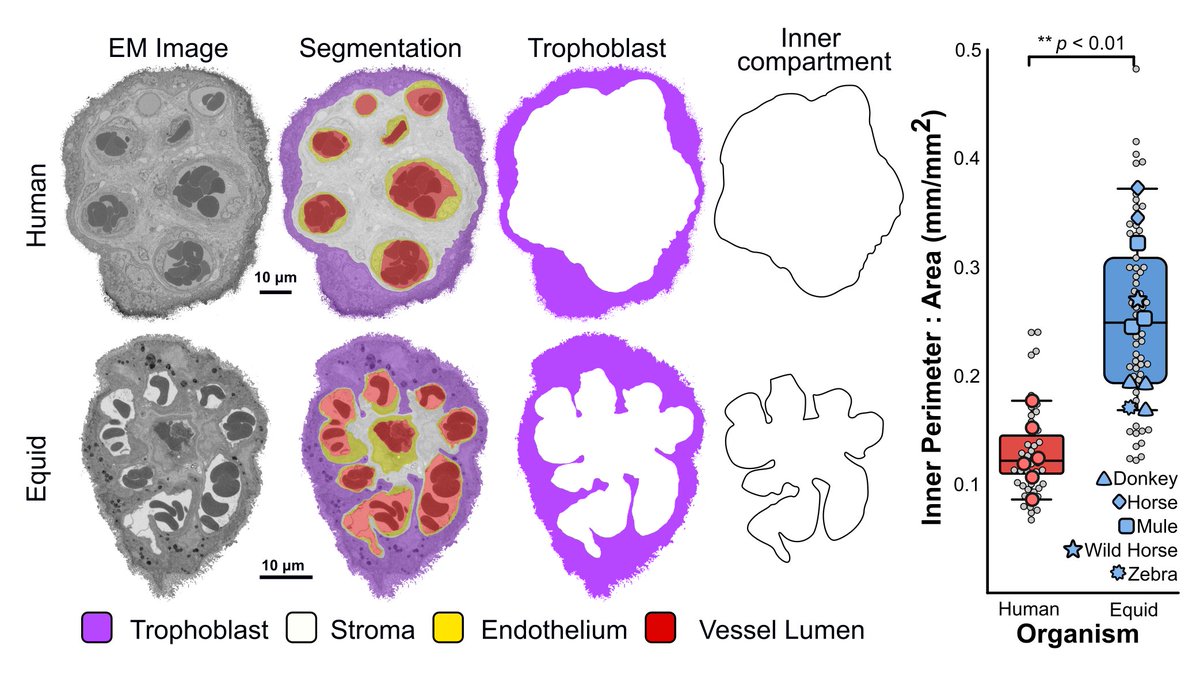
We then took correlative sub-volumes for #SBFSEM electron microscopy and found that equid villi display deep trophoblast protrusions surrounding blood vessels not seen in humans. BIU Southampton James Thompson Tricia Goggin

#microCT XRH & #ElectronMicroscopy are great technologies, but they are not much without the user's vision and imagination. Here's an example from the fab Davis Laundon.
Merry Christmas one and all!
BIU Southampton University Hospital Southampton 💙 Southampton Medicine nxct University of Southampton

Check out this fascinating review. Placenta is a vital organ that plays a role in the transmission of epigenetic assays traits from parents to the offspring.


Really chuffed with this paper. Amazing work from Davis Laundon but also includes project work carried out by Olivia Beasley for #MResEvolution University of Southampton Biological Sciences

Our latest review 'Placental evolution from a three-dimensional and multiscale structural perspective' was selected as the Editor's Choice article for January's issue of Evolution Journal! Check it out below 👇